In today’s rapidly evolving industrial sectors such as automotive, rail, wind energy, and industrial automation, precise sensing capabilities and mechanical stability are of critical importance. Sensor bearings have been developed specifically to address these demands. Unlike traditional bearings, sensor bearings integrate mechanical performance with intelligent sensing technology, enabling precise monitoring of speed, position, temperature, or vibration within rotating systems. This helps manufacturers reduce system complexity, enhance performance, and collect real-time critical machine data.
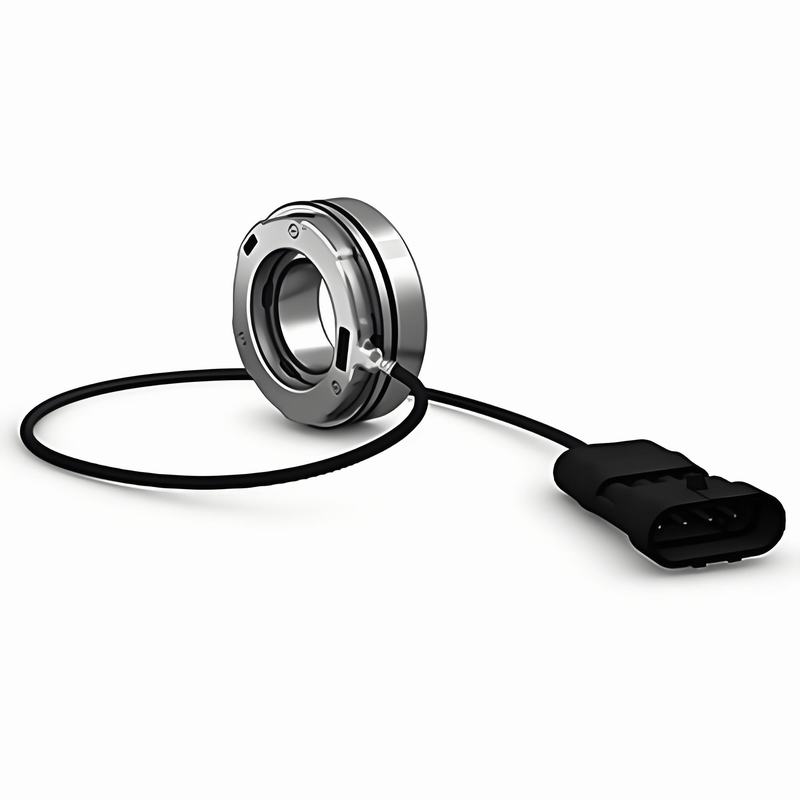

Sensor bearings are multifunctional components that integrate precision bearings with built-in sensors to measure parameters such as rotational speed, direction, position, or temperature. By reducing the need for external components, sensor bearings enhance system intelligence and are widely used in applications such as automotive anti-lock braking systems, wind turbines, railway equipment, and industrial machinery.
In this guide, we will delve into the zasady działania, advantages, common applications, and why NYZ is a trusted supplier for global buyers.
What are sensor bearings?
Sensor bearings are mechanical bearings integrated with sensors. These sensors can measure physical parameters such as speed, angle, torque, or temperature and transmit real-time data to the control system. Depending on the application, different types of sensors may be used inside the bearing:
Hall effect sensors: Measure speed and direction by detecting magnetic fields.
Optical sensors: Determine position or rotation using light and reflectors.
Inductive sensors: Detect motion in conjunction with metal targets.
Temperature sensors (e.g., Pt100 thermistors): Monitor bearing temperature.
Each sensor bearing unit typically includes a sensor module, signal conditioning unit, and signal transmission interface (wired or wireless).
Since the sensors are directly integrated into the bearing, this design saves space, reduces installation time, and simplifies system maintenance.
How do sensor bearings work?
The typical structure of a sensor bearing includes an inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements (such as balls or rollers), sensor module, magnetic ring (encoder), and signal processing circuitry. Its standard operating principle primarily involves two core functions:
Speed and direction detection
A magnetized ring is installed on the rotating component of the bearing (such as the shaft). When the shaft rotates, the sensor chip detects changes in the magnetic field via the Hall effect and converts these changes into electrical pulses, thereby indicating rotational speed and direction. The electrical signals are then transmitted to the electronic control unit (ECU) or industrial monitoring system for real-time feedback and system adjustment.
Temperature Monitoring
High-precision temperature sensors, such as Pt100 thermistors, are embedded within the bearing. When the bearing generates heat under heavy loads, the sensors continuously monitor the temperature and transmit the data to the monitoring system to trigger overheating alarms or activate cooling systems.
Thanks to this design, sensor bearings not only provide high-performance rotational support but also endow mechanical systems with sensing capabilities, making them a key component in the transition to smart manufacturing.
What are the application areas of sensor bearings?
Sensor bearings have widespread applications across various industries, with common application scenarios including:
Automotive Industry
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Wheel speed sensors embedded in hub bearings help prevent wheel lockup during braking.
Electric Power Steering (EPS): Torque and angle sensors enhance steering control.
Electric Vehicles (EV): Monitor rotor speed and load to optimize motor performance.
Wind turbines
Sensor bearings monitor the temperature and vibration of turbine main shafts or gearboxes, enabling early detection of issues such as wear, overheating, or imbalance, thereby reducing downtime and improving the operational efficiency and availability of wind farms.
Railways
In railway vehicles, sensor bearings are used for wheel speed detection, axle temperature monitoring, and condition-based warning systems. They help maintenance teams predict failures, extend maintenance intervals, and ensure operational safety.
Industrial Automation
Robotic arms and CNC machine tools rely on sensor bearings for precise angle and motion control, with applications including gearboxes, drive shafts, and conveyor rollers.
What are the advantages of sensor bearings?
Compared to traditional systems that require separate sensors, sensor bearings offer numerous advantages, including:
Compact design
By integrating sensors with bearings, the system becomes smaller and more lightweight. No additional space is required for wiring or external sensor installation, making it ideal for space-constrained systems such as electric vehicles and robots.
Reduced installation time
Pre-assembled units simplify system integration, reducing the need for wiring and mounting brackets, significantly shortening installation and maintenance time, and improving overall efficiency.
Real-time monitoring
Sensor bearings continuously monitor real-time data on critical parameters such as shaft speed, direction, temperature, or vibration, helping to detect anomalies early and prevent equipment failures and safety hazards.
Enhance automation and intelligence
When integrated with electronic control units or industrial control systems, sensor bearings can become part of a closed-loop control system, enabling more precise equipment management.
Multi-functional system integration and cost-effectiveness
Sensor bearings can be easily integrated with industrial programmable logic controllers (PLCs), automotive electronic control units, and wireless monitoring systems (via CAN bus, Bluetooth, etc.), offering excellent cost-effectiveness.