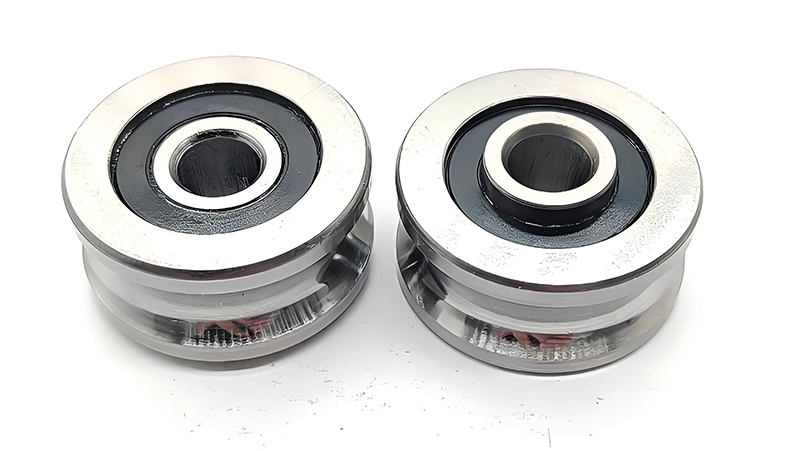
Spårkullager: En omfattande guide till deras funktion, struktur och tillämpningar
Djup groove
kullagerär viktiga mekaniska komponenter som möjliggör smidig och effektiv rörelse i en mängd olika applikationer.
I denna heltäckande guide kommer vi att fördjupa oss i grunderna för
spårkullager med djupa spåroch utforskar deras funktioner, tillämpningar, strukturer, tätningstyper, material, alternativ för radiellt spel och mycket mer.

Oavsett om du är en erfaren ingenjör eller en nyfiken entusiast syftar den här artikeln till att avmystifiera spårkullagrens värld och belysa deras avgörande roll inom maskinområdet.
Vad är spårkullager?
Spårkullager är en typ av kullager som
rullningslager utformad för att underlätta rotation av axlar och axlar samtidigt som friktionen minimeras.
Ingenjörer och branschfolk uppskattar dem för deras mångsidighet och förmåga att effektivt hantera både radiella och axiella belastningar.
Men eftersom de i första hand är konstruerade som radiallager är deras kapacitet för axiella belastningar är begränsad. Med andra ord klarar de betydligt högre radiella belastningar än axiella, vilket gör dem till förstahandsvalet för applikationer med höga radiella belastningar.
Enligt SKF, en välkänd tillverkare, kan spårkullager arbeta vid höga rotationshastigheter, eftersom ingenjörerna optimerar dem för låg ljudnivå och låga vibrationer.
Spårkullagrens funktioner
Spårkullagrens primära funktion är att bära radiella och axiella belastningar inom vissa gränser, och deras huvudsyfte är att minska friktionen i roterande utrustning.
Den
djupa spår gör det möjligt för lagren att motstå radiella och axiella belastningar i båda riktningarna, vilket gör dem lämpliga för applikationer där krafter verkar i två riktningar.
Dessutom konstruerar ingenjörerna spårkullager för höghastighetsdrift, och dessa lager kan också fungera vid en mängd olika hastigheter - vilket säkerställer stabil och pålitlig prestanda i olika miljöer.
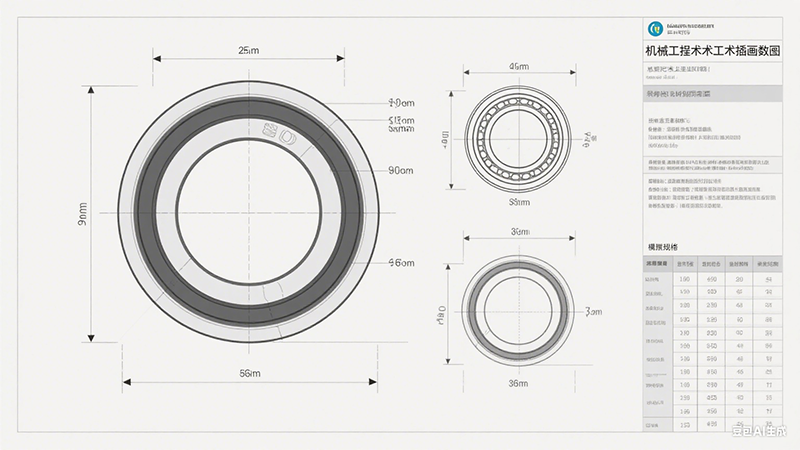
Struktur för spårkullager
Spårkullager har en enkel struktur som består av en yttre ring, en inre ring, en uppsättning kulor och en bur som håller kvar kulorna i löpbanorna.
Tätningstyper för spårkullager
Spårkullager finns i allmänhet i tre typer: öppen typ, avskärmad typ och tätad typ. Det specifika valet beror på applikationens behov, men lager av tätad typ är ofta att föredra för att förbättra prestanda och förlänga livslängden.
Ingenjörer och underhållspersonal kallar ofta skärmade och tätade lager för underhållsfria lager - en egenskap som gör dem mycket attraktiva för många applikationer.
1. Metallsköldar
Dessa sköldar, som även kallas beröringsfria tätningar, ger ett måttligt skydd mot kontaminering och är lämpliga för applikationer med låg risk för kontaminering. De är inte konstruerade för vattentålighet.
En metallsköld är fäst på den yttre ringen, medan den inre ringen har ett V-format spår och en labyrintspalt för att förhindra att damm tränger in och för att täta in fett.
2. Gummitätningar
Gummitätningar är väl lämpade för miljöer med höga föroreningsnivåer och ger ett förbättrat skydd mot damm, fukt och andra yttre faktorer.
Dessa tätningar kategoriseras vanligtvis i två typer: kontaktfria och kontakt.
- Beröringsfria gummitätningar: Den yttre ringen på dessa tätningar är tillverkad av stålplattor gjutna med syntetiskt gummi. De blockerar effektivt damm och andra föroreningar men har dåligt vattenmotstånd.
- Kontakta gummitätningar: Dessa är mycket lika kontaktfria gummitätningar, men deras kanter har konstant kontakt med det V-formade spåret på innerringens yta. Denna design gör dem till det optimala valet för applikationer med hög kontaminering, eftersom de förhindrar att föroreningar - även vatten - tränger in i fettet.
Material för spårkullager
Valet av material för spårkullager är avgörande för deras prestanda och livslängd.
Tillverkarna använder oftast högkvalitativt stål för de inre och yttre ringarna, medan de kan tillverka kulorna av stål, keramik eller andra avancerade material.
Exempelvis erbjuder keramiska kulor fördelar som minskad friktion, ökad styvhet och korrosionsbeständighet.
Som nämndes i föregående avsnitt kan tillverkarna göra tätningar av metall, men de använder en miljövänlig nitrilgummiblandning som det vanligaste tätningsmaterialet.
Alternativ för radiellt spel för spårkullager
Det radiella spelet - definierat som det inre mellanrummet mellan rullelementen och löpbanorna - är en nyckelfaktor för spårkullager. Det påverkar lagrets förmåga att ta upp värmeexpansion och felinställning.
Vanliga alternativ för radiellt spel inkluderar:
- CN (normal frigång): Lämplig för normala driftsförhållanden med måttliga hastigheter och temperaturer.
- C3 (större spelrum än normalt): Utformad för applikationer med högre temperaturer eller hastigheter, vilket möjliggör termisk expansion.
- C4 (större än C3 frigång): Används i extrema högtemperatur- eller höghastighetsförhållanden och tar även upp värmeutvidgning.
- C0 (snävare spelrum): Idealisk för applikationer som kräver minimalt radiellt spel.
Användningsområden för spårkullager
Industrier och maskintillverkare använder spårkullager i stor utsträckning inom olika sektorer och utrustningstyper.
Från fordonssystem och elmotorer till hushållsapparater och industrimaskiner, dessa
Lagren spelar en nyckelroll för att säkerställa en sömlös rörelse.
Professionella inom olika branscher tillskriver deras utbredda användning till deras effektivitet, hållbarhet och anpassningsförmåga till olika driftsförhållanden.
Viktiga tillämpningar inkluderar:
- Fordonsindustrin: Hjulnav, växellådor, elmotorer, motorkomponenter
- Elektriska motorer: AC- och DC-motorer, generatorer, växelströmsgeneratorer
- Industriella maskiner: Transportörsystem, fläktar och blåsmaskiner, pumpar, kompressorer
- Hushållsapparater: Tvättmaskiner, kylskåp, luftkonditioneringsapparater, dammsugare
- Flyg- och rymdindustrin: Landningsställ för flygplan, styrsystem för flygplan
- Gruvutrustning: Transportband, krossar, kvarnar
- Elverktyg: Borrmaskiner, slipmaskiner, slipmaskiner
- Medicinsk utrustning: Tandläkarborrar, utrustning för medicinsk avbildning
- Textilmaskiner: Spinnmaskiner, vävstolar
- Lantbruksmaskiner: Traktorer, skördetröskor, såmaskiner
- Anläggningsmaskiner: Grävmaskiner, bulldozers, kranar
- Utrustning för materialhantering: Gaffeltruckar, transportörer, lyfttruckar
- Järnvägsapplikationer: Lokomotiv, komponenter till järnvägsfordon
- Olje- och gasindustrin: Pumpar, kompressorer, borrutrustning
- Marin industri: Framdrivningssystem, vinschar, pumpar
- Förnybar energi: Vindkraftverk, solföljningssystem
- Fitnessutrustning: Träningsmaskiner, löpband, stationära cyklar
- Robotteknik: Robotarmar, automatiserade tillverkningssystem
- Instrumentering och mätutrustning: Precisionsinstrument, mätanordningar
- Livsmedels- och dryckesindustrin: Transportörsystem, förpackningsmaskiner
Denna lista är inte uttömmande, eftersom spårkullager är en oumbärlig del av driften av otaliga mekaniska system i alla branscher. Deras mångsidighet, effektivitet och förmåga att motstå olika belastningar gör dem till en hörnsten inom maskin- och teknikområdet.
Slutsats
Sammanfattningsvis är spårkullager ryggraden i effektiva maskiner, med en perfekt balans mellan mångsidighet och tillförlitlighet.
Från deras grundläggande struktur till de invecklade detaljerna i tätningstyper och radiella spelalternativ - att förstå nyanserna i dessa lager är avgörande för att optimera deras prestanda i olika applikationer.
När du påbörjar din resa för att utnyttja kraften i rörelse, står spårkullager redo att driva dina maskiner mot en framtid med sömlös och effektiv drift.

